Electronics and communications Engineering comprise of designing, testing of electronics equipment and researching different systems. It also covers the broadcast systems. Due to Electronics and Communications Engineering the World has become small.in Electronics we read the smallest part of equipment like IC’s, basic electronics about digital signal, Analog signal etc.
. The chapter covers in Electronics and communication Engineering are as follows:In the Electronic Devices and circuit, we study about diode, semiconductor Diodes, semiconductor Material, p-n Junction Diode, Zennor Diode, Doping, Forward Biased Voltage AC Resistance etc. In the Electronics Device and circuit, A Diode is semiconductor device which plays vital role in the electronics systems. The ideal diode is open- circuit in the region of non-conductor and short-circuit for region of conduction. The semiconductor material having doping process is known as extrinsic material. There are two types extrinsic material found in semiconductor device is :- n-type and p-type. n-type semiconductor material is formed by doping impurity elements having five valance electrons such as arsenic, phosphorous and antimony. p-type semiconductor material is formed by doping of pure Ga or Si crystal with impurity atoms having three valance electrons.
Microprocessor is an integrated circuit that fabricated on the small chip which will perform the Arithmetic Logical Unit operations.
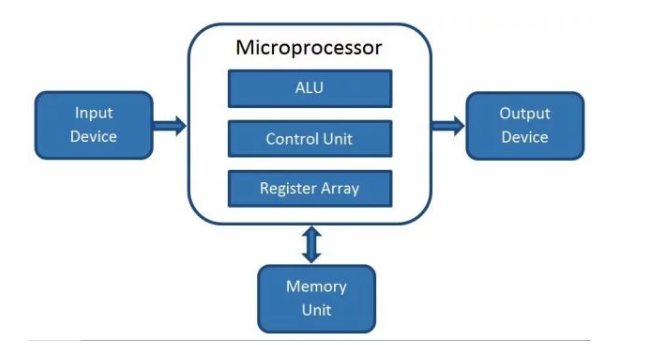
The working of the microprocessor is that it will take input value from device, process them as per instruction passed and give the result as output. Microprocessor is the brain of computer which made up of ALU, Register and CU(control Unit).
Advantages of Microprocessor are as below:Some of important terms used in the Microprocessor are Bus, Word Length, Cache Memory, Clock Speed.
The very first microcontroller was invented by Intel Corp. The 8-bit microcontroller was introduced by the Intel Corp. is known as 8051. 8051 Microcontroller is single chip microcomputer that is made by fabrication of VLSI. It is called as embedded controller as its support are also built into it. There are many words length of microcontroller are available i.e 4bit, 8bit, 16bit, 32bit and 128bit.

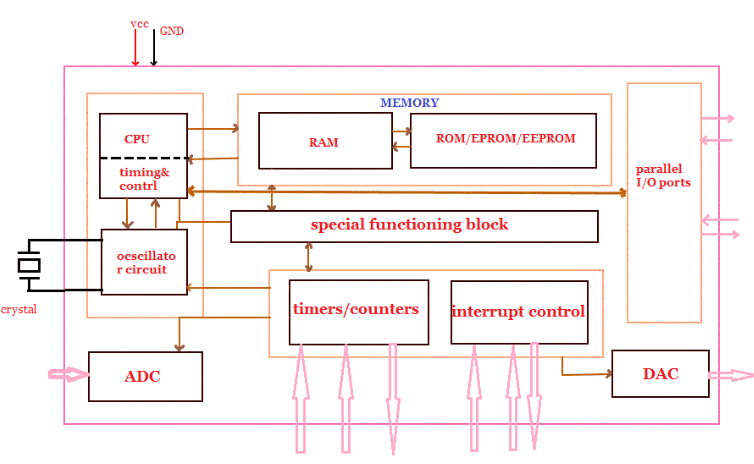 Fig:- Block diagram of microcontroller and Basic structure
Fig:- Block diagram of microcontroller and Basic structure
In Signal and Systems we study about Sinusoidal signals for discrete time and continuous time. We always consider numbers of distinctions between discrete time and continuous time sinusoidal signals. We know that continuous time signals is periodic. The exponential signals is one the class of the signals.
In the above signal it is showing that Continuous-time sinusoidal signal of frequency, amplitude and phase.Communication is the process of transfer information from one place to another. In other words, we can say that communication is process of exchanging the information’s between two individuals. Like wise, Analog communication is the way of conveying i.e receiving, sending and processing the information with voice, image, text etc by the continuous signals and analog signals. We know that continuous signals is sinusoidal in nature so it has continuous time and amplitude. For the communication purpose three systems are required
Sender -> Channel -> ReceiverHere Sender is the person who send the information which is also called as communicator. There are different ways of sending message like, voice, text, video, image etc
Channel: It is the medium by which the information send by the sender travels up to the Receiver.
Receiver: It is the person who receives the message or information sent by the communicator. The Receiver has no information to share.
There are two types of signals:It is the continuous signals whose properties changes over a time period. It is used to send the information from one place to other place by some medium. In the practical life, analog signal have distortion and noise when sending information from one place to another.
Digital Signal:It is non-continuous signal which is used to convey the message between sender and receiver. The information convey between sender and receiver by the collection of elements which works together.
Periodic Signal:The digital signal or Analog signal which continues itself after every interval of trime is call periodic signal. It is also called as deterministic signals.
Examples :- Square wave, sine wave, sawtooth wave, cos wave tec.NEW YEAR OFFER 50% OFF !!! Order Now
NEW YEAR OFFER 50% OFF !!
Lets take Best opinion from our Expert Tutors Today! Order Now
*Disclaimer: The reference papers provided by QuickAssignmentHelp.net serve as model papers for students and not to be submitted as it is. These papers are intended to used for research and reference purposes only.
Copyright © 2024 QuickAssignmentHelp.net All right reserved.